Introduction to Collaborative Robots
May 1, 2021
Topics include definitions and terminology of collaborative robots, a brief history, applications, advantages and disadvantages, and programming techniques.
Introduction to Collaborative Robots
In 2008 Universal Robots sold the first collaborative robot (cobot) to Linatex, a Danish supplier of technical plastics and rubber for industrial applications. This robot broke all preconceived ideas of how companies could integrate automation into the workplace. A collaborative robot works directly with humans in a defined space without the risk of a serious accident or severe injury. A cobot’s appeal isn’t just its collaborative element but also its quick installation and return on investment (ROI). The collaborative robot series has taken off in various industries, allowing further advancements in that technology and introducing it into non-manufacturing settings.
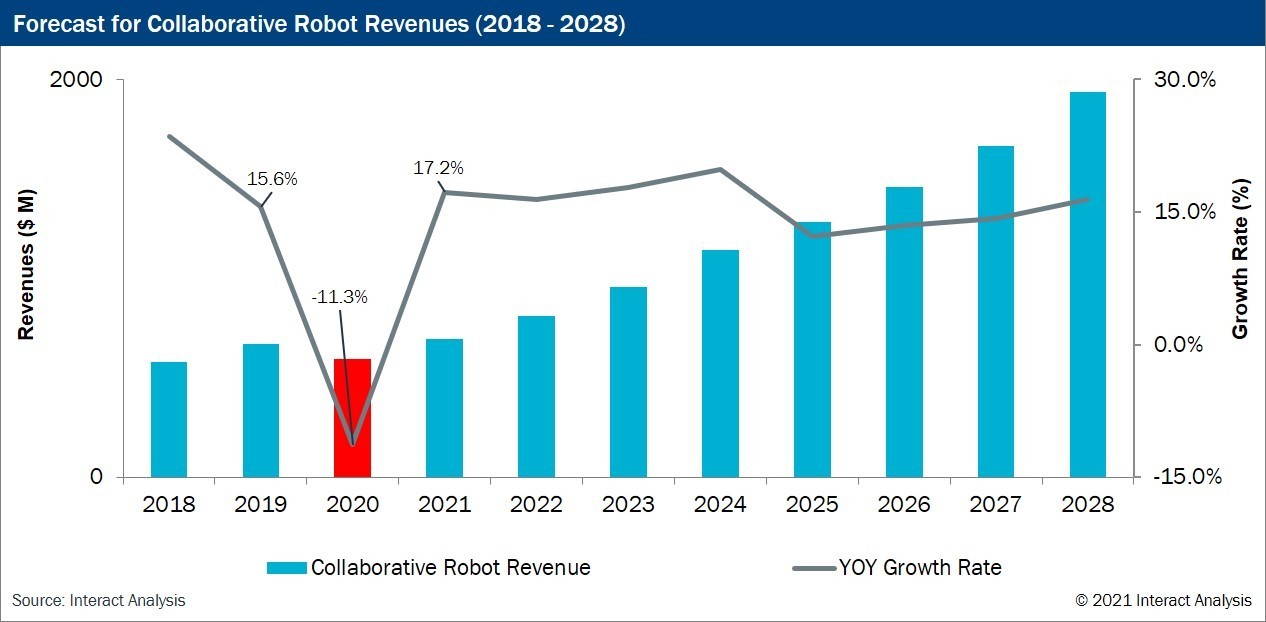
After its introduction, the collaborative robot sector saw explosive growth in the market. In 2019 collaborative robots’ global revenue was $669.9 million, with 22,459 robots shipped that year. The market continued to see success until the COVID-19 global pandemic hit, resulting in a sharp decrease in demand just like the rest of the robotic market. However, the market predicts a considerable rebound and will reach its most significant market growth rate in 2021 at 20%. The collaborative robot’s innovative design gives it the perks of an industrial robot while providing flexibility, safety, and affordability; making it the most popular robot on the market.
What Makes These Robots “Collaborative”
The innovative design of a cobot enables workers to safely interact with the robot in a collaborative space, with minimal risk of injuries or damages. Cobots achieve this high safety standard with a rounded design, safety-rated stop monitoring, force limitations, hand-guided programming, and a compact body. The collaborative robot’s stop-monitoring program detects intrusions and stops while occupying the robot’s work envelope. An example of this would be a worker entering the collaborative space to interact with the robot, triggering it to come to a complete stop until the worker clears the robot’s work envelope. The rounded design and force limitations also aid in a softer blow upon impact with workers, resulting in little to no injury.
Alongside safety features, collaborative robots offer users a state-of-the-art, yet friendly, programming interface. Workers can start using the collaborative robot after only a small amount of training. Programming for these robots is intuitive to the user because of its hand-guiding feature, also known as FreeDrive mode. The user can program the robot’s path by physically moving it to its desired positions. Collaborative Robot technology will progress further, seeing advancement as their scope of work continues to broaden.
Cobot Applications Expand as Technology Advances
Market analysts expect the collaborative robot market to continue to grow due to several factors:
- A shortage in qualified laborers (manufacturing skills gap)
- More industries investing in collaborative automation
- Higher demand for a product
- Need for flexibility in automated processes
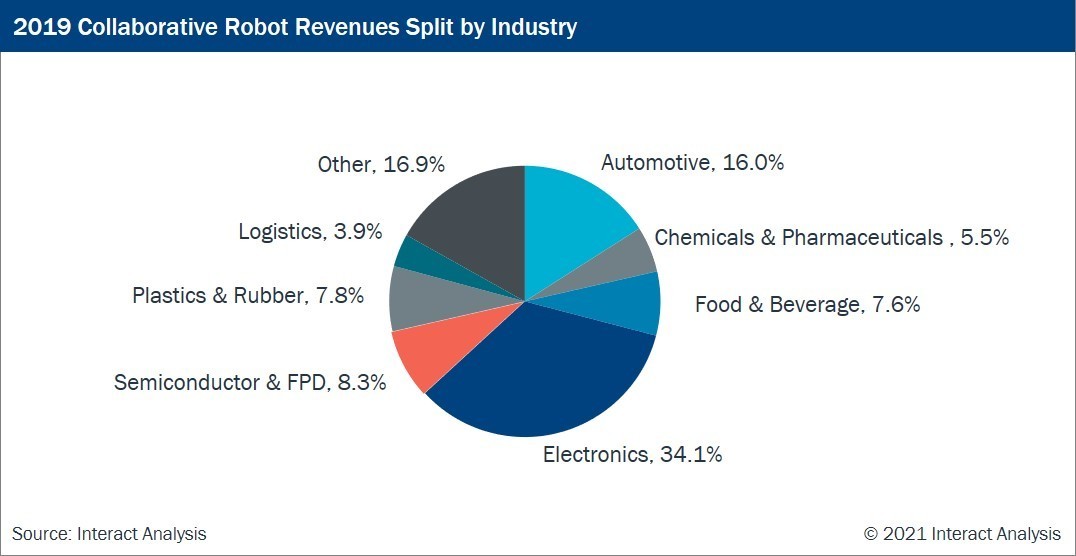
Small to medium-size businesses (SMBs) have been the biggest buyers of collaborative robots. The lower price point and a smaller initial investment of cobots naturally make for a better ROI. Their quick integration and flexibility allow SMBs to reduce downtime and non-productive activities during production hours. Advances in collaborative automation have led to new industries investing in robotic applications using cobots. Among these industries, the automotive and electronics sectors are expected to be the most significant collaborative robot users.
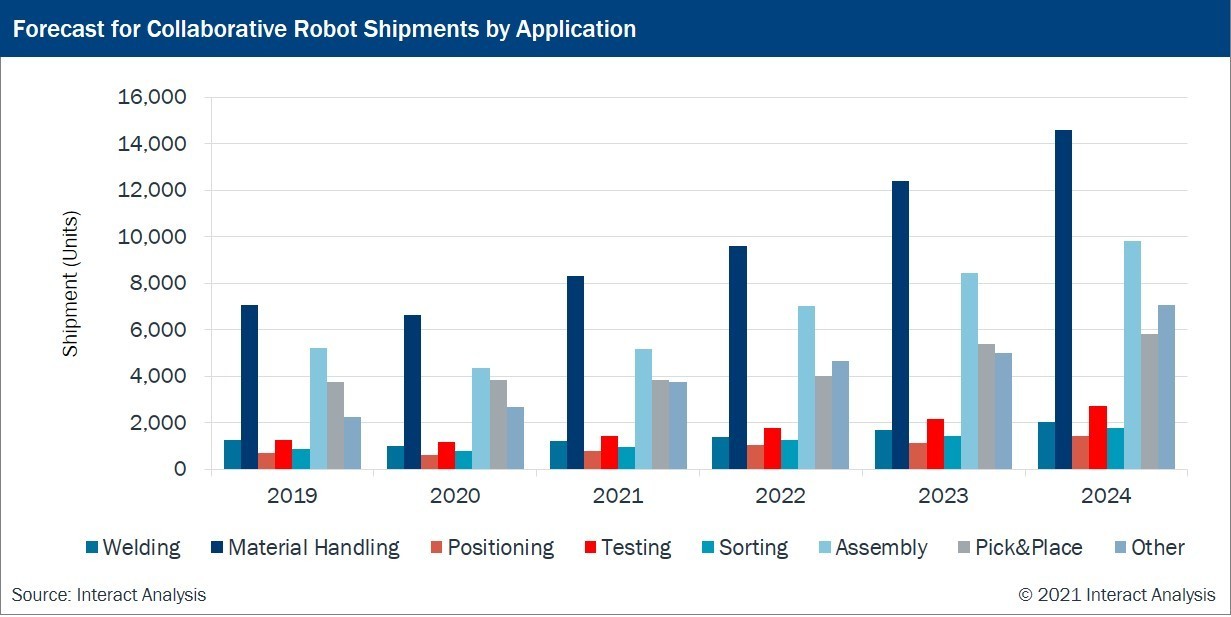
Companies are using collaborative robots for applications that are highly repetitive and require great precision. The three most popular applications performed by collaborative robots are materials handling, assembly, and pick & place. These applications attributed to 71.9% of collaborative robot revenues in 2019 and are predicted to hold a 62.7% share in 2024. However new industries investing in cobots have led to experimentation in different applications, especially outside manufacturing. A great example of this can be found in the healthcare industry, where cobots are being used to assist in surgeries and other medical areas. Other common applications performed by cobots include assembly, dispensing, finishing, machine tending, material handling, welding, material removal, quality inspections.
Are Cobots A Good Fit For Your Company?
Collaborative robots are popular for a good reason; however, they are not suitable for every situation. A company looking into collaborative automation would first need to determine the task they need to automate, the requirements that need to be met, risk assessment of the solution, and consult with an automation solutions provider. Many factors need to be considered when investing in an automated solution. While cobot technology is advancing at an accelerated rate, these robots still have certain limitations. With a compact design and slim build, these robots have a small payload and reach versus their industrial robot counterparts. Most common collaborative robots can only handle smaller payloads between 3 – 16 kg, with the highest payload limit being 35 kg. Another possible limitation of collaborative robots is their restricted speed. With safety being a top priority, speed is usually reduced to protect workers and limit the risk of impact. The best way to decide on whether collaborative automation is a good fit for your business is to answer these questions:
- What is the goal for automating?
- Is the facility a safe and desirable place for workers?
- Are the processes being automated fixed or changeable?
- Will the solution support manual processes or automate a complete manufacturing line?
- How much space does the facility have for automation equipment?
- What scalability requirements are there to support long-term growth?
- What is the payload, reach, accuracy, and cycle time requirements?
After answering all of these questions, a company can consult with an automation solutions provider to weigh the options and decide on the most beneficial solution.
Collaborative robots have gained a lot of popularity in the last few years for a good reason. Advancements in automation technology are making them useful in various applications, and the affordable initial investment makes them desirable across many industries (in and out of manufacturing). However, like any automated solution, it’s best to research and consult professionals before deciding if collaborative robots are the best solution for your business.
Related Articles
You might be also interested in:

- Featured
Latest Advancements in Material Cutting Robotics
Read about the latest technological advancements in robotic material cutting.

- Featured
Emerging 3D Vision Technologies for Industrial Robots
Learn about the emerging 3D vision technology that businesses are using for industrial robot applications.

- Featured
Most Popular Industrial Robotic Applications for 2021 and Projections
Explore the most popular application trends of 2021 and what to expect in the future.
Let's talk!
Request your quick quote today.
